Irish Bronze Age on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The prehistory of Ireland has been pieced together from
The prehistory of Ireland has been pieced together from  The two periods that have left the most spectacular groups of remains are the Neolithic, with its megalithic tombs, and the gold jewellery of the Bronze Age, when Ireland was a major centre of gold mining.
Ireland has many areas of bogland, and a great number of archaeological finds have been recovered from these. The anaerobic conditions sometimes preserve organic materials exceptionally well, as with a number of bog bodies, a Mesolithic
The two periods that have left the most spectacular groups of remains are the Neolithic, with its megalithic tombs, and the gold jewellery of the Bronze Age, when Ireland was a major centre of gold mining.
Ireland has many areas of bogland, and a great number of archaeological finds have been recovered from these. The anaerobic conditions sometimes preserve organic materials exceptionally well, as with a number of bog bodies, a Mesolithic
The Island of Ireland: Drowning the Myth of an Irish Land-bridge?
Accessed 21 December 2018. Snakes and most other reptiles could not repopulate Ireland because any land bridge disappeared before temperatures became warm enough for them. The lowered sea level also joined Britain to continental Europe; this persisted much longer, probably until around 5600 BC.Cunliffe, 2012, p. 56. The earliest known modern humans in Ireland date back to the late Palaeolithic Age (Old Stone Age). This date was pushed back some 2,500 years by a
/ref> The population has been tentatively estimated at around 8,000. The hunter-gatherers of the Mesolithic era lived on a varied diet of seafood, birds,
The hunter-gatherers of the Mesolithic era lived on a varied diet of seafood, birds,
 From around 4500 BC a Neolithic package that included cereal cultivars, housing culture (similar to those of the same period in Scotland) and stone monuments arrived in Ireland. Sheep, goats, cattle and cereals were imported from southwestern continental Europe, after which the population rose significantly. The earliest clear proof of farmers in Ireland or Great Britain is from Ferriter's Cove on the Dingle Peninsula, where a flint knife, cattle bones and a sheep's tooth were found and dated to c. 4350 BC. At the Céide Fields in
From around 4500 BC a Neolithic package that included cereal cultivars, housing culture (similar to those of the same period in Scotland) and stone monuments arrived in Ireland. Sheep, goats, cattle and cereals were imported from southwestern continental Europe, after which the population rose significantly. The earliest clear proof of farmers in Ireland or Great Britain is from Ferriter's Cove on the Dingle Peninsula, where a flint knife, cattle bones and a sheep's tooth were found and dated to c. 4350 BC. At the Céide Fields in
File:County Sligo - Creevykeel Court Tomb - 20190708134052.jpg,
 *
*
 The
The
 Metallurgy arrived in Ireland with new people, generally known as the
Metallurgy arrived in Ireland with new people, generally known as the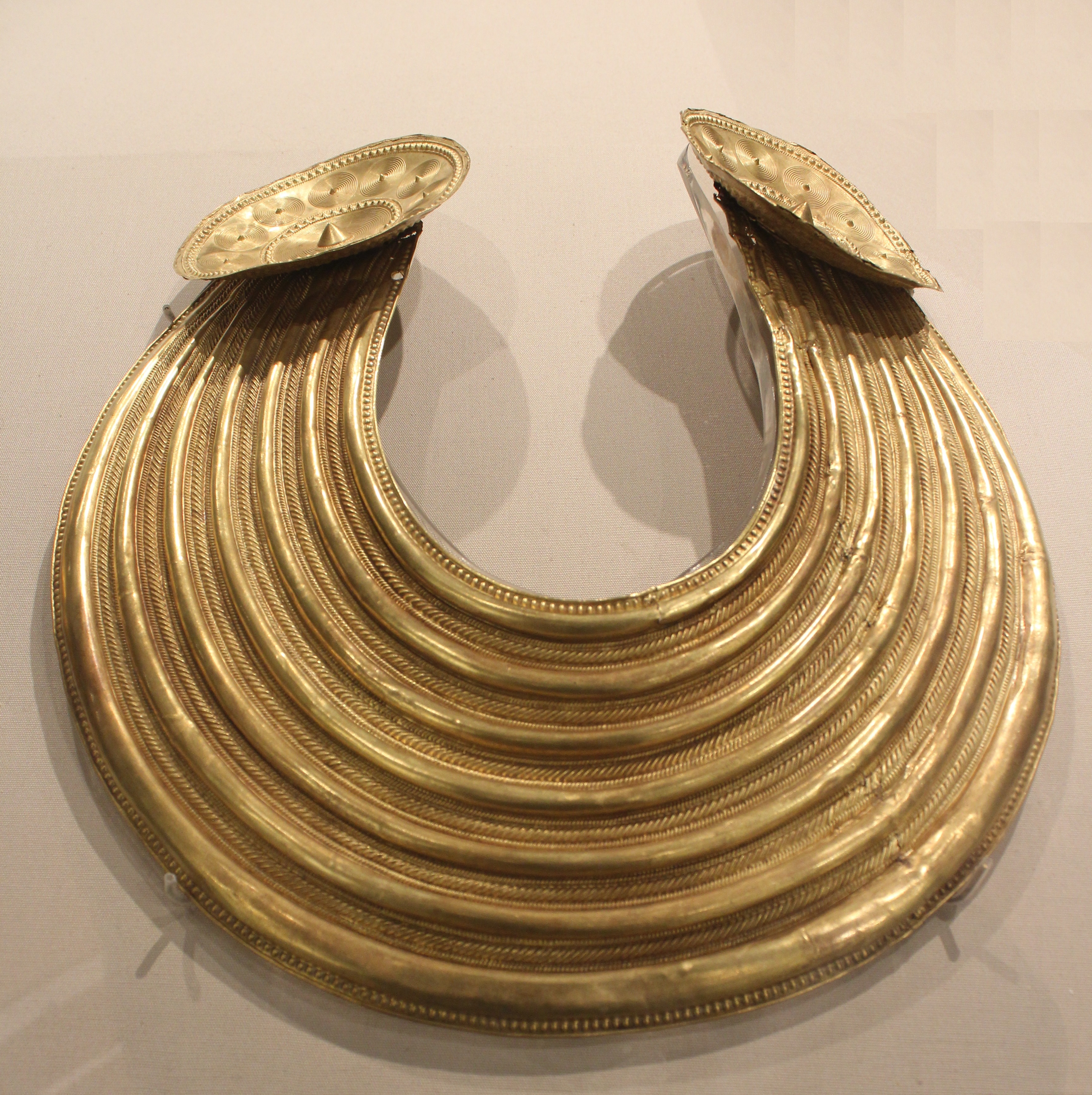  Copper used in the manufacture of bronze was mined in Ireland, chiefly in the southwest of the island, while the tin was imported from
Copper used in the manufacture of bronze was mined in Ireland, chiefly in the southwest of the island, while the tin was imported from  Construction of wedge tombs tailed off from about 2,200 BC,Wallace and O'Floinn, 51 and while the previous tradition of large scale monument building was much reduced, existing earlier megalithic monuments continued in use in the form of secondary insertions of funerary and ritual artefacts. Towards the end of the Bronze Age the single-grave cist made its appearance. This consisted of a small rectangular stone chest, covered with a stone slab and buried a short distance below the surface. The body might be cremated, or not. Decorated pots often accompanied the remains, and later cremated remains were placed inside the urn, which was turned upside-down, and might also have grave goods of various sorts. Numerous stone circles were also erected at this time, chiefly in Ulster and Munster.
Crannogs are timber homes built in shallow lakes for security, often with a narrow walkway to the shore. Some use or extend natural islets, and the largest probably housed a number of families, and animals. It is thought that most of the 1,200-odd crannogs in Ireland were begun in the Bronze Age, although many sites seem to have been used, continuously or intermittently, over very long periods, even into medieval times.
Construction of wedge tombs tailed off from about 2,200 BC,Wallace and O'Floinn, 51 and while the previous tradition of large scale monument building was much reduced, existing earlier megalithic monuments continued in use in the form of secondary insertions of funerary and ritual artefacts. Towards the end of the Bronze Age the single-grave cist made its appearance. This consisted of a small rectangular stone chest, covered with a stone slab and buried a short distance below the surface. The body might be cremated, or not. Decorated pots often accompanied the remains, and later cremated remains were placed inside the urn, which was turned upside-down, and might also have grave goods of various sorts. Numerous stone circles were also erected at this time, chiefly in Ulster and Munster.
Crannogs are timber homes built in shallow lakes for security, often with a narrow walkway to the shore. Some use or extend natural islets, and the largest probably housed a number of families, and animals. It is thought that most of the 1,200-odd crannogs in Ireland were begun in the Bronze Age, although many sites seem to have been used, continuously or intermittently, over very long periods, even into medieval times.
 The large Dowris Hoard, originally of over 200 items, mostly in bronze, has given its name to the Dowris Phase or period, as a term for the final phase of the Irish Bronze Age, about 900-600 BC. With 48 examples, the hoard contained all but two of the known examples of the distinctive "crotals", bronze rattles in the shape of a bull's
The large Dowris Hoard, originally of over 200 items, mostly in bronze, has given its name to the Dowris Phase or period, as a term for the final phase of the Irish Bronze Age, about 900-600 BC. With 48 examples, the hoard contained all but two of the known examples of the distinctive "crotals", bronze rattles in the shape of a bull's
File:DowrisHoard.jpg, Part of the Dowris Hoard
File:Flat bronze dagger (cropped).jpg, Tongue-shaped bronze dagger, Hunt Museum
File:Gold Dress Fastener of Clones in Co Monaghan (800-700 BC) in National Museum Dublin.jpg, Gold Dress Fastener,
 The Irish
The Irish  Examples from Iron Age Ireland of La Tène style, the term for Iron Age Celtic art, are very few, to a "puzzling" extent, although some of these are of very high quality, such as a number of scabbards from Ulster and the
Examples from Iron Age Ireland of La Tène style, the term for Iron Age Celtic art, are very few, to a "puzzling" extent, although some of these are of very high quality, such as a number of scabbards from Ulster and the  There are several ringforts in the complex topping the Hill of Tara, which seems to have its origins in the late Iron Age, although the site also includes a Neolithic passage grave and other earlier tombs. This is one of a number of major sites connected in later literature and mythology with kingship, and probably had a ritual and religious significance, though it is now impossible to be clear as to what this was.
There are several ringforts in the complex topping the Hill of Tara, which seems to have its origins in the late Iron Age, although the site also includes a Neolithic passage grave and other earlier tombs. This is one of a number of major sites connected in later literature and mythology with kingship, and probably had a ritual and religious significance, though it is now impossible to be clear as to what this was.
 The large areas of bog in Ireland have produced over a dozen ancient bog bodies, mostly from the Iron Age. Some were found and reburied before archaeological and scientific investigation was possible. Some survive as skeletons only, but the best-preserved have retained their flesh, hair, and clothing. The oldest appears to be the Neolithic
The large areas of bog in Ireland have produced over a dozen ancient bog bodies, mostly from the Iron Age. Some were found and reburied before archaeological and scientific investigation was possible. Some survive as skeletons only, but the best-preserved have retained their flesh, hair, and clothing. The oldest appears to be the Neolithic
''A History of Ireland in 100 Objects''
''
Driscoll, K. The Early Prehistory in the West of Ireland: Investigations into the Social Archaeology of the Mesolithic, West of the Shannon, Ireland (2006)
* Herity, M. and G. Eogan. Ireland in Prehistory. (1996) Routledge. * Ó Cróinín, Dáibhí, ed. (2008). ''A New History of Ireland: Prehistoric and early Ireland'', (Volume 1 series), Oxford University Press, . * Wallace, Patrick F., O'Floinn, Raghnall eds. ''Treasures of the National Museum of Ireland: Irish Antiquities'', 2002, Gill & Macmillan, Dublin, The book is chapters of text, followed by commentary on the illustrations and then a section with the illustrations, cross-referred by chapter and picture numbers, e.g. "3:13"
Driscoll, K. The Early Prehistory in the West of Ireland: Investigations into the Social Archaeology of the Mesolithic, West of the Shannon, Ireland (2006).
* Flanagan L. Ancient Ireland. Life before the Celts. (1998). * Thompson, T. ''Ireland’s Pre-Celtic Archaeological and Anthropological Heritage.'' (2006) Edwin Mellen Press. . * Waddell, J., ''The Celticization of the West: an Irish Perspective'', in C. Chevillot and A. Coffyn (eds), L' Age du Bronze Atlantique. Actes du 1er Colloque de Beynac, Beynac (1991), 349–366. * Waddell, J.,''The Question of the Celticization of Ireland'', Emania No. 9 (1991), 5–16. * Waddell, J., 'Celts, Celticisation and the Irish Bronze Age', in J. Waddell and E. Shee Twohig (eds.), ''Ireland in the Bronze Age''. Proceedings of the Dublin Conference, April 1995, 158–169.
Ask about Ireland, Flora and fauna
Postcards of the Prehistoric Monuments of Ireland
Treasures of early Irish art, 1500 B.C. to 1500 A.D.
an exhibition catalogue from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF)
Prehistoric Waterford
{{Europe topic , Prehistory of
 The prehistory of Ireland has been pieced together from
The prehistory of Ireland has been pieced together from archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
evidence, which has grown at an increasing rate over the last decades. It begins with the first evidence of permanent human residence in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
around 10,500 BC (although there is evidence of human presence as early as 31,000 BC) and finishes with the start of the historical record around 400 AD. Both the beginning and end dates of the period are later than for much of Europe and all of the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
. The prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
period covers the Palaeolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
, Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
, Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
, Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
societies of Ireland. For much of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, the historical record begins when the Romans invaded; as Ireland was not invaded by the Romans its historical record starts later, with the coming of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
.
wicker
Wicker is the oldest furniture making method known to history, dating as far back as 5,000 years ago. It was first documented in ancient Egypt using pliable plant material, but in modern times it is made from any pliable, easily woven material. ...
fish-trap, and a Bronze Age textile with delicate tassels of horse hair.
Glaciation and the Palaeolithic
During theLast Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
, ice sheets more than thick scoured the landscape of Ireland, by 24,000 years ago they extended beyond the southern coast of Ireland, by 16,000 years ago they had retreated so that only an ice bridge existed between Northern Ireland and Scotland, by 14,000 years ago Ireland was completely isolated from Britain and by 11,700 years ago this Glacial period is recognized as having ended with no more glaciers
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
present, but leaving Ireland as an arctic tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless moun ...
. This period's effects on Ireland are referred to as the Midlandian glaciation.
During the period between 17,500 and 12,000 years ago, a warmer period referred to as the Bølling-Allerød allowed for the rehabitation of northern areas of Europe by roaming hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s. Genetic evidence suggests this reoccupation began in southwestern Europe and faunal remains suggest the existence of a refugium in Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
that extended up into southern France
Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French language, French as , is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi ...
. Those originally attracted to the north during the pre- boreal period would be species like reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspe ...
and aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius'') ( or ) is an extinct cattle species, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of the largest herbivores in the Holocen ...
. Some sites as far north as Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
inhabited earlier than 10,000 years ago suggest that humans might have used glacial termini as places from which they hunted migratory game.
These factors and ecological changes brought humans to the edge of the northernmost ice-free zones of continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
by the onset of the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
and this included regions close to Ireland. However, during the early part of the Holocene Ireland itself had a climate that was inhospitable to most European animals and plants. Human occupation was unlikely, although fishing was possible.
Britain and Ireland may have been joined by a land bridge, but because this hypothetical link would have been cut by rising sea levels so early into the warm period, perhaps by 14,000 BC, few temperate terrestrial flora or fauna would have crossed into Ireland.Edwards, R.J., Brooks, A.J. (2008) "The Island of Ireland: Drowning the Myth of an Irish Land-bridge?" In: Davenport, J.J., Sleeman, D.P., Woodman, P.C. (eds.), ''Mind the Gap: Postglacial Colonisation of Ireland''. Special Supplement to ''The Irish Naturalists’ Journal'', pp 19-34,The Island of Ireland: Drowning the Myth of an Irish Land-bridge?
Accessed 21 December 2018. Snakes and most other reptiles could not repopulate Ireland because any land bridge disappeared before temperatures became warm enough for them. The lowered sea level also joined Britain to continental Europe; this persisted much longer, probably until around 5600 BC.Cunliffe, 2012, p. 56. The earliest known modern humans in Ireland date back to the late Palaeolithic Age (Old Stone Age). This date was pushed back some 2,500 years by a
radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
performed in 2016 on a bear bone excavated in 1903 in the "Alice and Gwendoline Cave
The Alice and Gwendoline Cave is a limestone cave in County Clare, Ireland. It is known as the site of brown bear bones bearing the mark of butchery, which have pushed back the first known human habitation of Ireland by over two thousand years.
...
", County Clare. The bone has cut marks showing it was butchered when fresh and gave a date of around 10,500 BC, showing humans were in Ireland at that time. In contrast, a flint worked by a human found in 1968 at Mell, Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth ...
, that is much older, probably well pre-dating 70,000 BC, is normally regarded as having been carried to Ireland on an ice sheet, probably from what is now the bottom of the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
. In 2021, a reindeer bone fragment discovered in Castlepook Cave near Doneraile
Doneraile (), historically Dunerayl, is a town in County Cork, Ireland. It is on the R581 regional road east of the N20 road, which runs from Limerick to Cork. It is about north of Mallow town. It is on the River Awbeg, a branch of the ...
, Co. Cork in 1972 was dated to 33,000 years ago, establishing human activity in Ireland more than 20,000 years earlier than previously thought.
A British site on the eastern coast of the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
, dated to 11,000 BC, indicated people were in the area eating a marine diet including shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater envir ...
. These modern humans may have also colonised Ireland after crossing a southern, now ice-free, land bridge that linked south-east Ireland and Cornwall, if it existed, or more likely, by boat. In the south, the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
facing South Wales was at the least a good deal narrower than today until 12,000 BC; in the north, the sea-crossing to Kintyre in Scotland, though much too deep to have ever been a land bridge, is even today only twelve miles at its shortest point and would then have been less. These people may have found few resources outside of coastal shellfishing and acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and borne ...
s, and so may not have continually occupied the region. The early coastline of Ireland is now almost entirely under the sea, so evidence of coastal populations is lost, though ways of investigating undersea sites are being explored.
The return of freezing conditions in the Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (c. 12,900 to 11,700 years BP) was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, c. 27,000 to 20,000 years BP). The Younger Dryas was the last stage ...
, which lasted from 10,900 BC to 9700 BC, may have depopulated Ireland. During the Younger Dryas, sea levels continued to rise and no ice-free land bridge between Great Britain and Ireland ever returned.
Mesolithic (8000–4000 BC)
The last ice age fully came to an end in Ireland about 8000 BC. Until the single 2016 Palaeolithic dating described above, the earliest evidence of human occupation after the retreat of the ice was dated to theMesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
(Middle Stone Age), around 7000 BC. Although sea levels were still lower than they are today, Ireland was very probably already an island by the time the first settlers arrived by boat, very likely from Britain. The earliest inhabitants of the island were seafarers who depended for much of their livelihood upon the sea, and later inland settlements or camps were usually close to water. Although archaeologists believe Mesolithic people heavily relied on riverine and coastal environments, ancient DNA indicates they had probably ceased contact with Mesolithic societies on the island of Britain and further afield.
Evidence for Mesolithic hunter-gatherers has been found throughout the island: a number of the key early Mesolithic excavations are the settlement site at Mount Sandel in Coleraine
Coleraine ( ; from ga, Cúil Rathain , 'nook of the ferns'Flanaghan, Deirdre & Laurence; ''Irish Place Names'', page 194. Gill & Macmillan, 2002. ) is a town and civil parish near the mouth of the River Bann in County Londonderry, Northern I ...
, County Londonderry
County Londonderry ( Ulster-Scots: ''Coontie Lunnonderrie''), also known as County Derry ( ga, Contae Dhoire), is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the thirty two counties of Ireland and one of the nine counties of Ulster. B ...
; the cremations at Hermitage, County Limerick on the bank of the River Shannon
The River Shannon ( ga, Abhainn na Sionainne, ', '), at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of the island of Ireland.
The Shan ...
; and the campsite at Lough Boora
Boora Bog (Irish ''Portach na Buaraí'') is a cutaway peat bog situated in County Offaly, Ireland.
Peat was harvested for fuel between the 1950s and 1970s, and the land is now being reclaimed for agricultural and eco-tourism use.
There was a l ...
in County Offaly
County Offaly (; ga, Contae Uíbh Fhailí) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in hono ...
. As well as these, early Mesolithic lithic
Lithic may refer to:
*Relating to stone tools
**Lithic analysis, the analysis of stone tools and other chipped stone artifacts
**Lithic core, the part of a stone which has had flakes removed from it
**Lithic flake, the portion of a rock removed to ...
scatters have been noted around the island, from the north in County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ga, Contae Dhún na nGall) is a county of Ireland in the province of Ulster and in the Northern and Western Region. It is named after the town of Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconne ...
to the south in County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns are ...
.Driscoll, K. The Early Prehistory in the West of Ireland: Investigations into the Social Archaeology of the Mesolithic, West of the Shannon, Ireland (2006)./ref> The population has been tentatively estimated at around 8,000.
wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
and hazelnut
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus ''Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species ''Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts according t ...
s. There is no evidence for deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer ...
in the Irish Mesolithic and it is likely that the first red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
were introduced in the early stages of the Neolithic. The human population hunted with spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fasten ...
s, arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
s and harpoon
A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument and tool used in fishing, whaling, seal hunting, sealing, and other marine hunting to catch and injure large fish or marine mammals such as seals and whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the t ...
s tipped with small stone blades called microliths, while supplementing their diet with gathered nut
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Com ...
s, fruit and berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, raspb ...
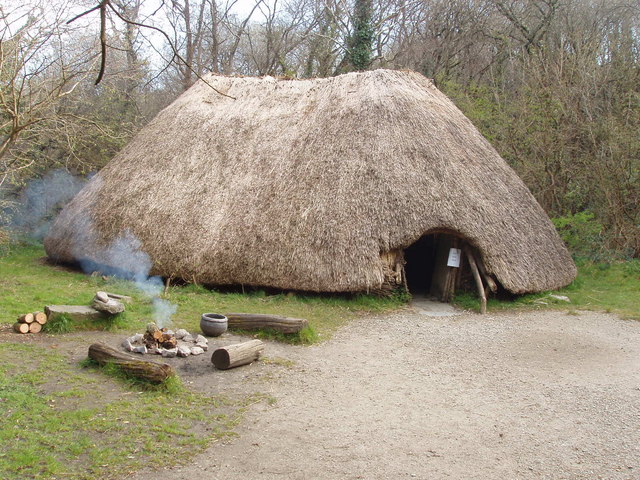
. They lived in seasonal shelters, which they constructed by stretching animal skins or thatch over wooden frames. They had outdoor hearth
A hearth () is the place in a home where a fire is or was traditionally kept for home heating and for cooking, usually constituted by at least a horizontal hearthstone and often enclosed to varying degrees by any combination of reredos (a lo ...
s for cooking their food. During the Mesolithic the population of Ireland was probably never more than a few thousand. Surviving artefacts include small microlith
A microlith is a small Rock (geology), stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia an ...
blades and points, and later larger stone tools and weapons, in particular the versatile Bann flake
A Bann flake is a large, butt-trimmed, leaf-shaped lithic blade of flint or chert, dating from the Late Mesolithic period of prehistoric Ireland, from around 4500 BC onwards. They are named after the river Bann in Northern Ireland where large num ...
.
Neolithic (4000–2500 BC)
Many areas of Europe entered theNeolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
(New Stone Age) with a 'package' of cereal cultivars, pastoral animals (domesticated oxen/cattle, sheep, goats), pottery, weaving, housing and burial cultures, which arrived simultaneously, a process that began in central Europe as LBK (Linear Pottery culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
) about 6000 BC. Within several hundred years this culture was present in northern France. An alternative Neolithic culture, La Hoguette
La Hoguette () is a commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France.
Archeology
La Hoguette is also the type site of the early Neolithic La Hoguette culture that is found mainly in association with Linear po ...
culture, that arrived in France's northwestern region appears to be a derivative of the Ibero Italian-Eastern Adriatic Impressed Cardial Ware culture (Cardium pottery
Cardium pottery or Cardial ware is a Neolithic decorative style that gets its name from the imprinting of the clay with the heart-shaped shell of the '' Corculum cardissa '', a member of the cockle family Cardiidae. These forms of pottery a ...
). The La Hoguette culture, like the western Cardial culture, raised sheep and goats more intensely. By 5100 BC there is evidence of dairy practices in southern England, and modern English cattle appear to be derived from "T1 Taurids" that were domesticated in the Aegean region shortly after the onset of the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
. These animals were probably derived from cattle from the Linear Pottery culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
. Around 4300 BC cattle arrived in northern Ireland during the late Mesolithic period. The red deer was introduced from Britain about this time.
 From around 4500 BC a Neolithic package that included cereal cultivars, housing culture (similar to those of the same period in Scotland) and stone monuments arrived in Ireland. Sheep, goats, cattle and cereals were imported from southwestern continental Europe, after which the population rose significantly. The earliest clear proof of farmers in Ireland or Great Britain is from Ferriter's Cove on the Dingle Peninsula, where a flint knife, cattle bones and a sheep's tooth were found and dated to c. 4350 BC. At the Céide Fields in
From around 4500 BC a Neolithic package that included cereal cultivars, housing culture (similar to those of the same period in Scotland) and stone monuments arrived in Ireland. Sheep, goats, cattle and cereals were imported from southwestern continental Europe, after which the population rose significantly. The earliest clear proof of farmers in Ireland or Great Britain is from Ferriter's Cove on the Dingle Peninsula, where a flint knife, cattle bones and a sheep's tooth were found and dated to c. 4350 BC. At the Céide Fields in County Mayo
County Mayo (; ga, Contae Mhaigh Eo, meaning "Plain of the Taxus baccata, yew trees") is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. In the West Region, Ireland, West of Ireland, in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Conn ...
, an extensive Neolithic field system (arguably the oldest known in the world) has been preserved beneath a blanket of peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
. Consisting of small fields separated from one another by dry-stone walls, the Céide Fields were farmed for several centuries between 3500 and 3000 BC. Wheat and barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
were the principal crops cultivated. Pottery made its appearance around the same time as agriculture. Ware similar to that found in northern Great Britain has been excavated in Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United King ...
(Lyle's Hill pottery) and in Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 ...
. Typical of this ware are wide-mouthed, round-bottomed bowls.
This follows a pattern similar to western Europe or gradual onset of Neolithic, such as seen in La Hoguette Culture of France and Iberia's Impressed Cardial Ware Culture. Cereal culture advance markedly slows north of France; certain cereal strains such as wheat were difficult to grow in cold climates—however, barley and German rye were suitable replacements. It can be speculated that the DQ2.5 aspect of the AH8.1
HLA A1-B8-DR3-DQ2 haplotype (Also: ''AH8.1'', ''COX'', ''Super B8'', ''ancestral MHC 8.1'' or ''8.1 ancestral haplotype'') is a multigene haplotype that covers a majority of the human major histocompatibility complex on chromosome 6 (not to be con ...
haplotype may have been involved in the slowing of cereal culture into Ireland, Scotland and Scandinavia since this haplotype confers susceptibility to a Triticeae protein induced disease as well as Type I diabetes and other autoimmune diseases that may have arisen as an indirect result of Neolithisation.
Some regions of Ireland showed patterns of pastoralism that indicated that some Neolithic peoples continued to move and indicates that pastoral activities dominated agrarian activities in many regions or that there was a division of labour between pastoral and agrarian aspects of the Neolithic. At the height of the Neolithic the population of the island was probably in excess of 100,000, and perhaps as high as 200,000. But there appears to have been an economic collapse around 2500 BC, and the population declined for a while.
Monuments
The most striking characteristic of the Neolithic in Ireland was the sudden appearance and dramatic proliferation of megalithic monuments. The largest of these tombs were clearly places of religious and ceremonial importance to the Neolithic population, and were probably communal graves used over a long period. In most of the tombs that have been excavated, human remains—usually, but not always, cremated—have been found. Grave goods—pottery, arrowheads, beads, pendants, axes, etc.—have also been uncovered. These megalithic tombs, more than 1,200 of which are now known, can be divided for the most part into four broad groups, all of which would originally have been covered with earth, that in many cases has been eroded away to leave the impressive stone frameworks: ;Types of Irish megalithic tombsCreevykeel Court Tomb
Creevykeel Court Tomb ( ga, Tuama Cúirte na Craobhaí Caoile) is one of the finest examples of a court tomb remaining in Ireland. The monument is located in the N15 Donegal to Sligo road, 50 meters north of Creevykeel cross-roads close to Cli ...
, a court cairn
The court cairn or court tomb is a megalithic type of chambered cairn or gallery grave. During the period, 3900–3500 BCE, more than 390 court cairns were built in Ireland and over 100 in southwest Scotland. The Neolithic (New Stone Age ...
in County Sligo
County Sligo ( , gle, Contae Shligigh) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the Border Region and is part of the province of Connacht. Sligo is the administrative capital and largest town in the county. Sligo County Council is the local ...
File:Knowth02.jpg, Knowth
Knowth (; ga, Cnóbha) is a Neolithic passage grave and an ancient monument of the World Heritage Site of Brú na Bóinne located 8.4 km west of Drogheda in Ireland's valley of the River Boyne. It is the largest passage grave of the Brú ...
, a passage tomb at Brú na Bóinne
(; 'Palace of the Boyne' or more properly 'Valley of the Boyne') or Boyne valley tombs, is an area in County Meath, Ireland, located in a bend of the River Boyne. It contains one of the world's most important prehistoric landscapes dating from ...
File:Pollnabrone.jpg, Poulnabrone dolmen
Poulnabrone dolmen (Poll na Brón in Irish) is an unusually large dolmen or portal tomb located in the Burren, County Clare, Ireland. Situated on one of the most desolate and highest points of the region, it comprises three standing portal ston ...
, a portal tomb in The Burren
File:11. Labbacallee Wedge Tomb, Co. Cork.jpg, Labbacallee wedge tomb
 *
*Court cairn
The court cairn or court tomb is a megalithic type of chambered cairn or gallery grave. During the period, 3900–3500 BCE, more than 390 court cairns were built in Ireland and over 100 in southwest Scotland. The Neolithic (New Stone Age ...
s – These are characterised by the presence of an entrance courtyard. They are found almost exclusively in the north of the island and are thought to include the oldest specimens. North Mayo has many examples of this type of megalith – Faulagh, Kilcommon, Erris.
* Passage tombs – These constitute the smallest group in terms of numbers, but they are the most impressive in terms of size and importance. They are also found in much of Europe, and in Ireland are distributed mainly through the north and east, the biggest and most impressive of them being found in the four great Neolithic "cemeteries" of the Boyne (Brú na Bóinne
(; 'Palace of the Boyne' or more properly 'Valley of the Boyne') or Boyne valley tombs, is an area in County Meath, Ireland, located in a bend of the River Boyne. It contains one of the world's most important prehistoric landscapes dating from ...
, a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
), Loughcrew (both in County Meath
County Meath (; gle, Contae na Mí or simply ) is a county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Ireland, within the province of Leinster. It is bordered by Dublin to the southeast, Louth to the northeast, Kildare to the south, Offaly to the sou ...
), Carrowkeel and Carrowmore (both in County Sligo
County Sligo ( , gle, Contae Shligigh) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the Border Region and is part of the province of Connacht. Sligo is the administrative capital and largest town in the county. Sligo County Council is the local ...
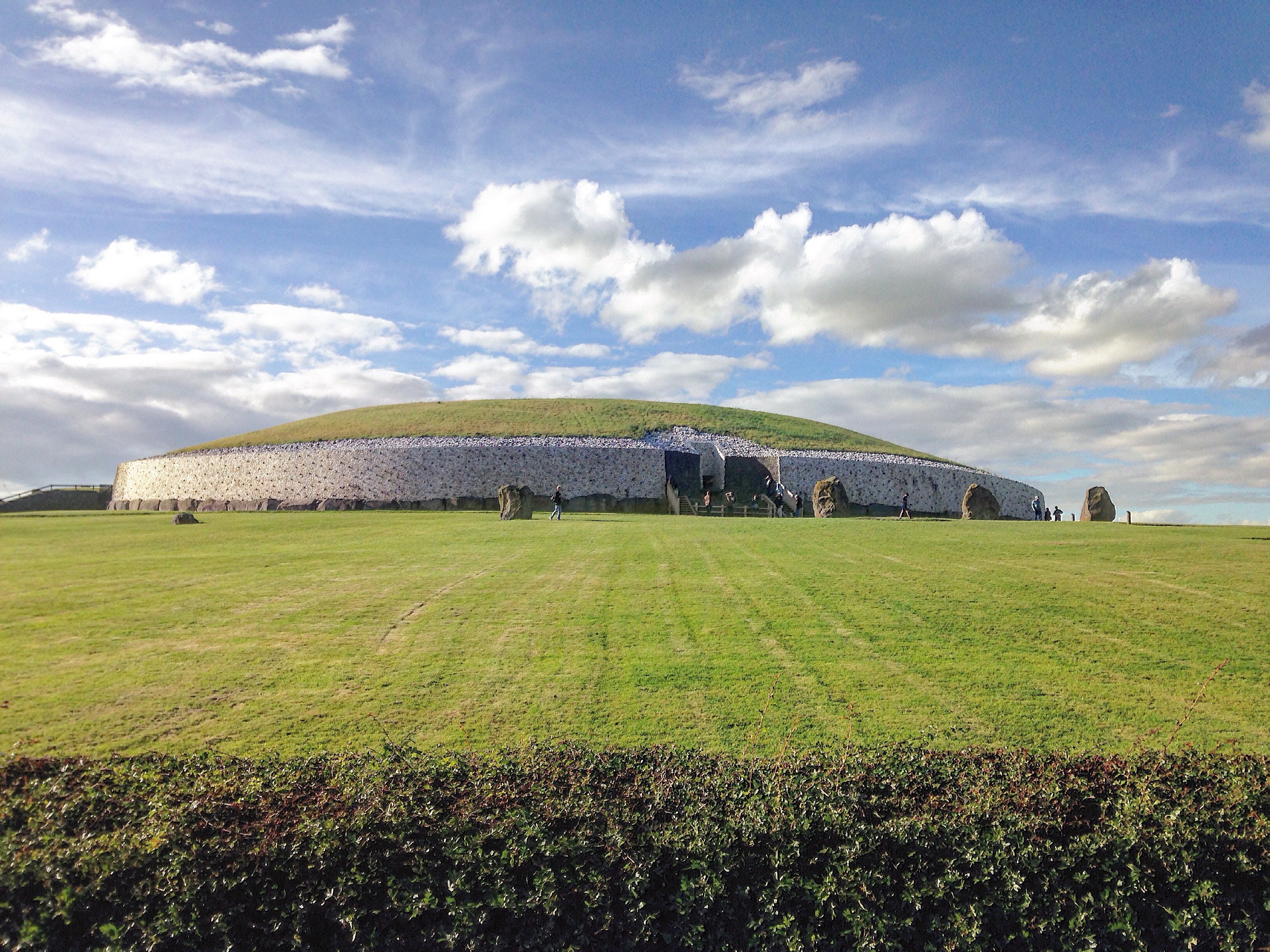
). The most famous of them is Newgrange
Newgrange ( ga, Sí an Bhrú) is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, located on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, west of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3200 BC, ...
, one of the oldest astronomically aligned monuments in the world. It was built around 3200 BC. At the winter solstice
The winter solstice, also called the hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the winte ...
the first rays of the rising sun still shine through a light-box above the entrance to the tomb and illuminate the burial chamber at the centre of the monument. Another of the Boyne megaliths, Knowth
Knowth (; ga, Cnóbha) is a Neolithic passage grave and an ancient monument of the World Heritage Site of Brú na Bóinne located 8.4 km west of Drogheda in Ireland's valley of the River Boyne. It is the largest passage grave of the Brú ...
, has been claimed to contain the world's earliest map of the Moon carved into stone.
* Portal tombs – These tombs include the well known dolmen
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
s. They consist of three or more upright stones supporting a large flat horizontal capstone (table). They were originally covered with earth to form a tumulus
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones buil ...
, but often their covering has now eroded to leave the impressive main stone structure. Most of them are to be found in two main concentrations, one in the southeast of the island and one in the north. The Knockeen and Gaulstown Dolmens in County Waterford are exceptional examples.
*Wedge tomb
A gallery grave is a form of megalithic tomb built primarily during the Neolithic Age in Europe in which the main gallery of the tomb is entered without first passing through an antechamber or hallway. There are at least four major types of galler ...
s – The largest and most widespread of the four groups, the wedge tombs are particularly common in the west and southwest. County Clare is exceptionally rich in them. They are the latest of the four types and belong to the end of the Neolithic. They are so called from their wedge-shaped burial chambers.
The theory that these four groups of monuments were associated with four separate waves of invading colonists still has its adherents today, but the growth in population that made them possible need not have been the result of colonisation: it may simply have been the natural consequence of the introduction of agriculture.
Portable artefacts
stone axe
A hand axe (or handaxe or Acheulean hand axe) is a prehistoric stone tool with two faces that is the longest-used tool in human history, yet there is no academic consensus on what they were used for. It is made from stone, usually flint or che ...
was the primary and essential tool for farming, carefully made in a variety of styles, and often polished. The products of axe factories next to sources of porcellanite
Porcellanite or ''porcelanite'', is a hard, dense Rock (geology), rock somewhat similar in appearance to unglazed porcelain. It is often an impure variety of chert containing clay and calcareous matter. Porcellanite has been found, for example, i ...
, an especially good stone, were traded across Ireland; the main ones were Tievebulliagh
Tievebulliagh () is a mountain in the Glens of Antrim, Northern Ireland. It forms part of the watershed between Glenaan to the north and Glenballyemon to the south. It is situated about 4.4 km from Cushendall.
Geology
Tievebulliagh is ...
and Rathlin Island
Rathlin Island ( ga, Reachlainn, ; Local Irish dialect: ''Reachraidh'', ; Scots: ''Racherie'') is an island and civil parish off the coast of County Antrim (of which it is part) in Northern Ireland. It is Northern Ireland's northernmost point. ...
, both in County Antrim
County Antrim (named after the town of Antrim, ) is one of six counties of Northern Ireland and one of the thirty-two counties of Ireland. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of and has a population o ...
. There were also imports from Britain, including products of the Langdale axe industry
The Langdale axe industry (or factory) is the name given by archaeologists to a Neolithic centre of specialised stone tool production in the Great Langdale area of the English Lake District. (For accompanying material seSupplement 1of same ...
of the English Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or ''fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
.
There was a much rarer class of imported prestige axe head made from jadeite
Jadeite is a pyroxene mineral with composition sodium, Naaluminium, Alsilicon, Si2oxygen, O6. It is hard (Mohs hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0), very tough, and dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. It is found in a wide range of colors, bu ...
from north Italy; these may have been slowly traded across Europe to reach Ireland over a period reaching into centuries, and show no signs of use. Miniature axes, too small to be useful, were made, and a "tiny porcellanite axe" has been found in a passage tomb; another example has a hole for a cord, and may have been worn as jewellery or an amulet
An amulet, also known as a good luck charm or phylactery, is an object believed to confer protection upon its possessor. The word "amulet" comes from the Latin word amuletum, which Pliny's ''Natural History'' describes as "an object that protects ...
. Other stone shapes made were chisel
A chisel is a tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge (such that wood chisels have lent part of their name to a particular grind) of blade on its end, for carving or cutting a hard material such as wood, stone, or metal by hand, stru ...
s, adzes, maces and spearheads. Only one decorated macehead has been found, in one of the tombs at Knowth
Knowth (; ga, Cnóbha) is a Neolithic passage grave and an ancient monument of the World Heritage Site of Brú na Bóinne located 8.4 km west of Drogheda in Ireland's valley of the River Boyne. It is the largest passage grave of the Brú ...
, but it is extremely fine. Some finds may also be miniature maceheads.
Pierced beads and pendants are found, and two necklaces of shells (from Phoenix Park
The Phoenix Park ( ga, Páirc an Fhionnuisce) is a large urban park in Dublin, Ireland, lying west of the city centre, north of the River Liffey. Its perimeter wall encloses of recreational space. It includes large areas of grassland and tre ...
in Dublin) are very carefully made, with graded periwinkle shells; these were on the remains of two males. As an example of the exceptional preservation sometimes possible in items found in anaerobic bogs, part of a finely woven bag with circular handles has survived; it used reedy plant material wound round thin strips of wood. Decorated pottery, apparently made for funerary
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture ...
rather than domestic use, appears to imitate basketry patterns.
Open-air rock art
Open-air rock art is another monument type that dates to the Late Neolithic or Early Bronze Age. These carvings are found on open-air boulders and outcrops and the most common motifs are cup and ring marks and radial grooves. This art is often referred to as Atlantic rock art due its similarity to other carvings across Atlantic Europe. In Ireland, the art appears in clusters with the most significant concentrations inCounty Fermanagh
County Fermanagh ( ; ) is one of the thirty-two counties of Ireland, one of the nine counties of Ulster and one of the six counties of Northern Ireland.
The county covers an area of 1,691 km2 (653 sq mi) and has a population of 61,805 a ...
and County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ga, Contae Dhún na nGall) is a county of Ireland in the province of Ulster and in the Northern and Western Region. It is named after the town of Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconne ...
, County Wicklow
County Wicklow ( ; ga, Contae Chill Mhantáin ) is a county in Ireland. The last of the traditional 32 counties, having been formed as late as 1606, it is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is bordered by t ...
and County Carlow
County Carlow ( ; ga, Contae Cheatharlach) is a county located in the South-East Region of Ireland, within the province of Leinster. Carlow is the second smallest and the third least populous of Ireland's 32 traditional counties. Carlow Cou ...
, County Louth
County Louth ( ; ga, An Lú) is a coastal county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Ireland, within the province of Leinster. Louth is bordered by the counties of Meath to the south, Monaghan to the west, Armagh to the north and Down to the ...
and County Monaghan, Cork, and Kerry. The densest clusters are on the Iveragh and Dingle peninsulas in Kerry.
Copper and Bronze Ages (2500–500 BC)
 Metallurgy arrived in Ireland with new people, generally known as the
Metallurgy arrived in Ireland with new people, generally known as the Bell Beaker
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from ar ...
People from their characteristic pottery, in the shape of an inverted bell. This was quite different from the finely made, round-bottomed pottery of the Neolithic. It is found, for example, at Ross Island
Ross Island is an island formed by four volcanoes in the Ross Sea near the continent of Antarctica, off the coast of Victoria Land in McMurdo Sound. Ross Island lies within the boundaries of Ross Dependency, an area of Antarctica claimed by New ...
, and associated with copper mining there, which had begun by at least 2,400 BC. There is some disagreement about when speakers of a Celtic language first arrived in Ireland. It is thought by some scholars to be associated with the Beaker People of the Bronze Age, but the more mainstream view is, or at least used to be, that "Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
" arrived much later at the beginning of the Iron Age.
The Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
began once copper was alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
ed with tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
to produce true bronze artefacts, and this took place around 2000 BC, when some "Ballybeg-type" flat axes and associated metalwork were produced. The tin needed to be imported, normally from Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
. The period preceding this, in which Lough Ravel and most Ballybeg axes were produced, and which is known as the Copper Age
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
or Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
, commenced about 2500 BC.
Bronze was used for the manufacture of both weapons and tools. Swords, axes, daggers, hatchets, halberds, awls, drinking utensils and horn-shaped trumpets are just some of the items that have been unearthed at Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
sites. Irish craftsmen became particularly noted for the horn-shaped trumpet, which was made by the ''cire perdue'', or lost wax
Lost-wax casting (also called "investment casting", "precision casting", or ''cire perdue'' which has been adopted into English from the French, ) is the process by which a duplicate metal sculpture (often silver, gold, brass, or bronze) is ...
, process.
 Copper used in the manufacture of bronze was mined in Ireland, chiefly in the southwest of the island, while the tin was imported from
Copper used in the manufacture of bronze was mined in Ireland, chiefly in the southwest of the island, while the tin was imported from Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
in Britain. The earliest known copper mine in these islands was located at ''Ross Island'', at the Lakes of Killarney
The Lakes of Killarney are a scenic attraction located in Killarney National Park near Killarney, County Kerry, in Ireland. They consist of three lakes - Lough Leane, Muckross Lake (also called Middle Lake) and Upper Lake.
Surroundings
The l ...
in County Kerry
County Kerry ( gle, Contae Chiarraí) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the South-West Region and forms part of the province of Munster. It is named after the Ciarraige who lived in part of the present county. The population of the co ...
; mining and metalworking took place there between 2400 and 1800 BC. Another of Europe's best-preserved copper mines has been discovered at Mount Gabriel in County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns are ...
, which was worked for several centuries in the middle of the second millennium. Mines in Cork and Kerry are believed to have produced as much as 370 tonnes of copper during the Bronze Age.
Ireland was also rich in native gold, and the Bronze Age saw the first extensive working of this precious metal by Irish craftsmen. More Bronze Age gold hoards have been discovered in Ireland than anywhere else in Europe. Irish gold ornaments have been found as far afield as Germany and Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
, and gold-related trade was very possibly a major factor in the Bronze Age Irish economy.
In the early stages of the Bronze Age the gold ornaments included simple but finely decorated gold lunulae, a distinctively Irish type of object later made in Britain and continental Europe, and disks of thin gold sheet. Many of these seem to have been long in use before they were deposited. Later the thin twisted torc made its appearance; this was a collar consisting of a bar or ribbon of metal, twisted into a spiral. Other types of gold jewellery made in Ireland during the Bronze Age, most shared with Britain, include earrings, sun disks, bracelets, clothes fasteners, and in the Late Bronze Age, the distinctively Irish large "gorgets", and ''bullae'' amulets. After the Bronze Age goldwork almost ceased to be produced in Ireland; the Irish deposits may well have been essentially exhausted.
 Construction of wedge tombs tailed off from about 2,200 BC,Wallace and O'Floinn, 51 and while the previous tradition of large scale monument building was much reduced, existing earlier megalithic monuments continued in use in the form of secondary insertions of funerary and ritual artefacts. Towards the end of the Bronze Age the single-grave cist made its appearance. This consisted of a small rectangular stone chest, covered with a stone slab and buried a short distance below the surface. The body might be cremated, or not. Decorated pots often accompanied the remains, and later cremated remains were placed inside the urn, which was turned upside-down, and might also have grave goods of various sorts. Numerous stone circles were also erected at this time, chiefly in Ulster and Munster.
Crannogs are timber homes built in shallow lakes for security, often with a narrow walkway to the shore. Some use or extend natural islets, and the largest probably housed a number of families, and animals. It is thought that most of the 1,200-odd crannogs in Ireland were begun in the Bronze Age, although many sites seem to have been used, continuously or intermittently, over very long periods, even into medieval times.
Construction of wedge tombs tailed off from about 2,200 BC,Wallace and O'Floinn, 51 and while the previous tradition of large scale monument building was much reduced, existing earlier megalithic monuments continued in use in the form of secondary insertions of funerary and ritual artefacts. Towards the end of the Bronze Age the single-grave cist made its appearance. This consisted of a small rectangular stone chest, covered with a stone slab and buried a short distance below the surface. The body might be cremated, or not. Decorated pots often accompanied the remains, and later cremated remains were placed inside the urn, which was turned upside-down, and might also have grave goods of various sorts. Numerous stone circles were also erected at this time, chiefly in Ulster and Munster.
Crannogs are timber homes built in shallow lakes for security, often with a narrow walkway to the shore. Some use or extend natural islets, and the largest probably housed a number of families, and animals. It is thought that most of the 1,200-odd crannogs in Ireland were begun in the Bronze Age, although many sites seem to have been used, continuously or intermittently, over very long periods, even into medieval times.
testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testostero ...
, as well as 26 horns or trumpets, weapons, and vessels. The rather earlier Dunaverney flesh-hook
The Dunaverney Flesh-Hook is a sophisticated bronze artefact from Prehistoric Ireland, thought to be an item of ceremonial feasting gear, and a symbol of authority. It is believed it was used to remove chunks of meat from a stew in a large cauldr ...
(perhaps 1050–900 BC) is suggestive of a culture where elite feasting was important, and reflects influence from continental Europe; very large riveted bronze cauldrons were also made. Large numbers of bronze weapons were produced, and typical sword shapes changed from shorter ones for stabbing and thrusting on foot, to longer ones, perhaps for a mounted warrior to slash with. This is one example of a Dowris Phase design type originating in the Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European Archaeological culture, culture of Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe ...
of continental Europe, probably transmitted via southern Britain; chapes for scabbards is another.
During the Bronze Age, the climate of Ireland deteriorated and extensive deforestation took place. The population of Ireland at the end of the Bronze Age was probably in excess of 100,000, and may have been as high as 200,000. It is possible that it was not much greater than it had been at the height of the Neolithic. In Ireland the Bronze Age lasted until c. 500 BC, later than continental Europe and also Britain.
Clones, County Monaghan
Clones ( ; , meaning 'meadow of Eois') is a small town in western County Monaghan, Ireland. The area is part of the Border Region, earmarked for economic development by the Irish Government due to its currently below-average economic situation ...
, 800-700 BC
File:Bronze Age bracelet from Castlederg.jpg, Late Bronze Age bracelet from Castlederg
Castlederg (earlier Caslanadergy, ) is a town in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland. It lies on the River Derg and is near the border with County Donegal, Ireland. It stands in the townlands of Castlesessagh and Churchtown, in the historic barony ...
, c. 950-800 BC
File:Gold collar ( 800-700 BC) from Co Clare (detail).jpg, Late Bronze Age gold "gorget", 800-700 BC, found in County Clare. NMI, Dublin
Iron Age (500 BC–AD 400)
 The Irish
The Irish Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
has long been thought to begin around 500 BC and then continue until the Christian era in Ireland, which brought some written records and therefore the end of prehistoric Ireland. This view has been somewhat upset by the recent carbon-dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
of the wood shaft of a very elegant iron spearhead found in the River Inny near Lackan
Lackan () is a townland in County Westmeath, Ireland. It is located about north-north–west of Mullingar.
Lackan is one of 10 townlands of the civil parish of Lackan in the barony of Corkaree in the Province of Leinster. The townland covers ...
, which gave a date of between 811 and 673 BC. This may further erode the belief, still held by some, that the arrival of iron-working marked the beginning of the arrival of the Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
(i.e. speakers of the Proto-Celtic language) and thus Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
speakers, to the island.
Alternatively, many hold the view that this happened with the bearers of the Bell Beaker culture, probably Indo-European speaking, reaching Ireland during the earlier stage of the Bronze Age. The Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
of Britain and Ireland, also known as Insular Celtic
Insular Celtic languages are the group of Celtic languages of Brittany, Great Britain, Ireland, and the Isle of Man. All surviving Celtic languages are in the Insular group, including Breton, which is spoken on continental Europe in Brittany, ...
, can be divided into two groups, Goidelic
The Goidelic or Gaelic languages ( ga, teangacha Gaelacha; gd, cànanan Goidhealach; gv, çhengaghyn Gaelgagh) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historically ...
and Brittonic. When primary written records of Celtic first appear in about the fifth century, Gaelic or Goidelic, in the form of Primitive Irish
Primitive Irish or Archaic Irish ( ga, Gaeilge Ársa), also called Proto-Goidelic, is the oldest known form of the Goidelic languages. It is known only from fragments, mostly personal names, inscribed on stone in the ogham alphabet in Ireland ...
, is found in Ireland, while Brittonic, in the form of Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a ...
, is found in Britain.
The Iron Age includes the period in which the Romans ruled most of the neighbouring island of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
. Roman interest in the area led to some of the earliest written evidence about Ireland. The names of its tribes were recorded by the geographer Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD.
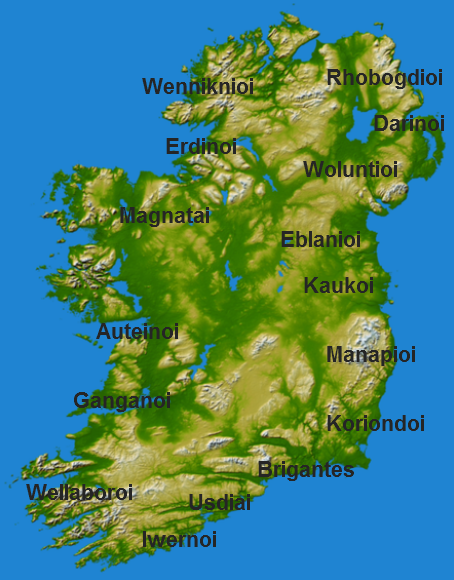
The recorded tribes of Ireland included at least three with names identical or similar to British or Gaulish tribes: the Brigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geogr ...
(also the name of the largest tribe in northern and midland Britain), the Manapii
The Manapii are an ancient tribe from southeastern Ireland mentioned by Greek geographer Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD.
They were later attested as '' (Fir) Manach'' (var. ''Manaig'', ''Monaig'') in the Early Christian period, a tribe dwelling fu ...
(possibly the same people as the Menapii
The Menapii were a Belgic tribe dwelling near the North Sea, around present-day Cassel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name Attestations
They are mentioned as ''Menapii'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Orosius (early 5th c. AD), ...
, a Belgic tribe of northern Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
) and the Coriondi
The Coriondi (Κοριονδοί) were a people of early Ireland, referred to in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'' as living in southern Leinster.T. F. O'Rahilly, ''Early Irish History and Mythology'', Dublin Institute for Ad ...
(a name similar to that of Corinion, later Cirencester and the Corionototae
The Corionototae were a group of Ancient Britons apparently inhabiting what is now Northern England about whom very little is known. They were recorded in one Roman votary inscription (now lost) from Corbridge, of uncertain date, which commemorate ...
of northern Britain).
Up to about 150 BC there are many finds that show stylistic influence from continental Europe (as in the preceding Dowris Phase), and some direct imports. After that date relationships with British styles predominate, perhaps reflecting some movement of people. The Keshcarrigan Bowl
The Keshcarrigan Bowl is an Iron Age bronze bowl discovered to the north of Keshcarrigan, County Leitrim, Ireland, in the 19th century. The bowl was found in the waterway between Lough Scur and Lough Marrave ("lake of death"). It was perhaps a ...
, possibly made in Britain, is an example of this. Another cup found in Fore, County Westmeath
Fore () is a village, next to the old Benedictine Abbey ruin of Fore Abbey, situated to the north of Lough Lene in County Westmeath, in Ireland.
The village, (sister parish of nearby St. Mary's Collinstown) is situated within a valley between ...
does seem to be an import.
Petrie Crown
Petrie is a surname of Scottish origin which may refer to:
People
* Alexander Petrie (died 1662), Scottish minister
* Alistair Petrie (born 1970), English actor
* Andrew Petrie (1798–1872), Scottish-born builder, architect and first free settle ...
, apparently dating to the 2nd century AD. This was well after Celtic art elsewhere had been subsumed into Gallo-Roman art and its British equivalent. Despite this it was in Ireland that the style seemed to revive in the early Christian period, to form the Insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, was produced in the post-Roman era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term derives from ''insula'', the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style dif ...
of the Book of Kells
The Book of Kells ( la, Codex Cenannensis; ga, Leabhar Cheanannais; Dublin, Trinity College Library, MS A. I. 8 sometimes known as the Book of Columba) is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New ...
and other well-known masterpieces, perhaps under influence from Late Roman and post-Roman Romano-British styles. The 1st century BC Broighter Gold
The Broighter Gold or more correctly, the Broighter Hoard, is a hoard of gold artefacts from the Iron Age of the 1st century BC that were found in 1896 by Tom Nicholl and James Morrow on farmland near Limavady, in the north of Ireland (now North ...
hoard, from Ulster, includes a small model boat, a spectacular torc with relief decoration influenced by classical style, and other gold jewellery probably imported from the Roman world, perhaps as far away as Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
.
The headland of Drumanagh
Drumanagh (Irish ''Droim Meánach'') is a headland near the village of Loughshinny, in the north east of Dublin, Ireland. It features an early 19th-century Martello tower and a large (200,000 m²) Iron Age promontory fort which has produced Rom ...
, near Dublin and not yet fully excavated, may have represented a centre for trade with Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was ...
. Drumanagh is an example of the coastal promontory fort
A promontory fort is a defensive structure located above a steep cliff, often only connected to the mainland by a small neck of land, thus using the topography to reduce the ramparts needed. Although their dating is problematic, most seem to da ...
, using cliff headlands with a narrow neck to reduce the extent of fortification necessary. In Ireland these seem to be mainly a feature of the Iron Age,Wallace and O'Floinn, 126 with some perhaps dating to the Bronze Age, and also continuing to be used into the Early Medieval period. Although today seen as mostly dating from the early historic period, some of the perhaps 60,000 ringfort
Ringforts, ring forts or ring fortresses are circular fortified settlements that were mostly built during the Bronze Age up to about the year 1000. They are found in Northern Europe, especially in Ireland. There are also many in South Wales ...
s or raths in Ireland date back to the Late Iron Age. These vary greatly in size and function, with smaller ones a single-family farmstead (with slaves), or merely an enclosure for animals, and larger ones clearly having a wider political and military significance.
Navan Fort
Navan Fort ( sga, Emain Macha ; ga, Eamhain Mhacha, label= Modern Irish ) is an ancient ceremonial monument near Armagh, Northern Ireland. According to tradition it was one of the great royal sites of pre-Christian Gaelic Ireland and the cap ...
(''Emain Macha''), another major hilltop site, had a very large circular building constructed on it about 100 BC. It was forty metres across, with 275 tree-posts in rings. The largest was the central post, a tree felled about 95 BC. Within the century following the whole building was destroyed, apparently in a ritual fashion.
Other large-scale constructions, requiring a good degree of social organization, include linear earthworks such as the Black Pig's Dyke and Cliadh Dubh, probably representing boundaries, and acting as hindrances to cattle-raids, and "toghers" or wooden trackways across boggy areas, of which the best-known is the Corlea Trackway
__NOTOC__
The Corlea Trackway () is an Iron Age trackway, or ''togher'', near the village of Keenagh, south of Longford, County Longford, in Ireland. It was known locally as the ''Danes' Road''. It was constructed from oak planks in 148–147 ...
, a corduroy road
A corduroy road or log road is a type of road or timber trackway made by placing logs, perpendicular to the direction of the road over a low or swampy area. The result is an improvement over impassable mud or dirt roads, yet rough in the bes ...
dated to 148-147 BC, and about a kilometre long and some three metres wide.
Irish Dark Age (100 BC–AD 300)
The late Iron Age saw sizeable changes in human activity. Thomas Charles-Edwards coined the phrase "Irish Dark Age" to refer to a period of apparent economic and cultural stagnation in late prehistoric Ireland, lasting from c. 100 BC to c. AD 300. He used the phrase to describe a gap in the archaeological record coinciding with theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
in Britain and continental Europe. Charles-Edwards notes the lack of continuity between Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's writings on the peoples of second-century Ireland and writings in ogham in the fifth century. He suggested that the decrease in agricultural productivity might be due to a large-scale export of slaves to Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was ...
.
Others such as Joseph Raftery, Barry Raftery
Barry Raftery (16 August 1944 – 22 August 2010) was an Irish archaeologist and academic. He is best known for his pioneering work in wetland archaeology and Iron Age hillforts in Ireland. He was Professor of Celtic Archaeology in University Col ...
, and Donnchadh Ó Corráin have drawn attention to a decline in human settlement and activity in Ireland, starting from around the first century BC. Pollen data extracted from Irish bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; a ...
s indicate a decrease in human impact on plant life in the bogs in the third century, and specifically that "the impact of human activity upon the flora around the bogs from which the pollen came was less between c. 200 BC and c. AD 300 than either before or after."Charles-Edwards, p. 148. The third and fourth centuries saw a rapid recovery.
The reasons for the decline and recovery are uncertain, but it has been suggested that recovery may be linked to the "Golden Age" of Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was ...
in the third and fourth centuries. The archaeological evidence for trade with, or raids on, Roman Britain is strongest in northern Leinster
Leinster ( ; ga, Laighin or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, situated in the southeast and east of Ireland. The province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige. Following the 12th-century Norman invasion of Ir ...
, centred on modern County Dublin
"Action to match our speech"
, image_map = Island_of_Ireland_location_map_Dublin.svg
, map_alt = map showing County Dublin as a small area of darker green on the east coast within the lighter green background of ...
, followed by the coast of County Antrim
County Antrim (named after the town of Antrim, ) is one of six counties of Northern Ireland and one of the thirty-two counties of Ireland. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of and has a population o ...
, with lesser concentrations in the Rosses on the north coast of County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ga, Contae Dhún na nGall) is a county of Ireland in the province of Ulster and in the Northern and Western Region. It is named after the town of Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconne ...
and around Carlingford Lough
Carlingford Lough (, Ulster Scots: ''Carlinford Loch'') is a glacial fjord or sea inlet in northeastern Ireland, forming part of the border between Northern Ireland to the north and the Republic of Ireland to the south. On its northern shore i ...
. As Roman Britain collapsed politically, there was even settlement by Irish people, and leaders, in Wales and western Britain. Inhumation
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
burials may also have spread from Roman Britain, and had become common in Ireland by the fourth and fifth centuries.
Some protohistoric
Protohistory is a period between prehistory and history during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing, but other cultures have already noted the existence of those pre-literate groups in their own writings. For example, in ...
records begin to appear during this period. Early Irish literature was not written down until the Early Medieval period, but many scholars accept that the saga cycles preserve in some form elements from much earlier, that give some insights into the world of the last elites of prehistoric Ireland.
Bog bodies
 The large areas of bog in Ireland have produced over a dozen ancient bog bodies, mostly from the Iron Age. Some were found and reburied before archaeological and scientific investigation was possible. Some survive as skeletons only, but the best-preserved have retained their flesh, hair, and clothing. The oldest appears to be the Neolithic
The large areas of bog in Ireland have produced over a dozen ancient bog bodies, mostly from the Iron Age. Some were found and reburied before archaeological and scientific investigation was possible. Some survive as skeletons only, but the best-preserved have retained their flesh, hair, and clothing. The oldest appears to be the Neolithic Stoneyisland Man
Stoneyisland Man is the name given to a bog body discovered in the Stoneyisland Bog, Gortanumera, County Galway, Ireland on 13 May 1929.
Discovery
Turf-cutters James Dolphin, Thomas Rodgers and John Spain uncovered a human skeleton while working ...
, perhaps the victim of a canoeing accident around 3320–3220 BC.
Cashel Man
Cashel Man is a bog body from a bog near Cashel in County Laois, Ireland. He was found on 10 August 2011 by Bord na Móna employee Jason Phelan from Abbeyleix. The body was a young adult male, around 20–25,Hart, Edward, dir. "Ghosts of Murde ...
died violently about 2500-2000 BC in the early Bronze Age, and is one of the possible ritual killings; it is now thought these were deposed kings sacrificed after being seen to fail in their rule, perhaps after crop failures. Two Iron Age examples of apparent elite victims of ritual killing are Old Croghan Man and Clonycavan Man
Clonycavan Man is the name given to a well-preserved Iron Age bog body found in Clonycavan, Ballivor, County Meath, Ireland in March 2003. The body shows signs of having been murdered. Theories around the meanings and manner of his death vary. ...
, both from approximately 400 to 175 BC. Earlier bodies appear to have been normal burials.
Collections
Almost all prehistoric Irish finds remain in theBritish Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
. Some are in local museums, but much the most significant collections are in Dublin, Belfast and London. The first "national" collection for Irish antiquities was the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
in London, where many finds from before and after it was established in 1753 have ended up. However, from the foundation of the Dublin Royal Irish Academy
The Royal Irish Academy (RIA; ga, Acadamh Ríoga na hÉireann), based in Dublin, is an academic body that promotes study in the sciences, humanities and social sciences. It is Ireland's premier List of Irish learned societies, learned socie ...
in 1785 there was a local rival, which became the main destination of objects that were newly-found, or appeared on the market. The Dublin Society
The Royal Dublin Society (RDS) ( ga, Cumann Ríoga Bhaile Átha Cliath) is an Irish philanthropic organisation and members club which was founded as the 'Dublin Society' on 25 June 1731 with the aim to see Ireland thrive culturally and economi ...
also formed a collection, though this was less important for antiquities. The society was founded in 1731, and by 1733 had opened a museum. Both these collections were transferred to the new "Museum of Science and Art", now the National Museum of Ireland
The National Museum of Ireland ( ga, Ard-Mhúsaem na hÉireann) is Ireland's leading museum institution, with a strong emphasis on national and some international archaeology, Irish history, Irish art, culture, and natural history. It has thre ...
, by 1890.
A legal dispute in which the Crown challenged the British Museum's purchase of the Broighter Hoard
The Broighter Gold or more correctly, the Broighter Hoard, is a hoard of gold artefacts from the Iron Age of the 1st century BC that were found in 1896 by Tom Nicholl and James Morrow on farmland near Limavady, in the north of Ireland (now Nort ...
was won in 1903, and marked the acceptance on all sides of the Dublin museum as the Irish national collection.Wallace and O'Floinn, 8 This was a hoard found in what became Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
after Irish independence. Northern Ireland had seen its many important finds of antiquities passing to first London and then Dublin, and the Ulster Museum
The Ulster Museum, located in the Botanic Gardens in Belfast, has around 8,000 square metres (90,000 sq. ft.) of public display space, featuring material from the collections of fine art and applied art, archaeology, ethnography, treasure ...
was only recognized as a national museum for antiquities in 1961. This had developed out of the collections of the Belfast Natural History Society, later renamed the Belfast Municipal Museum and Art Gallery, and was renamed again in 1961. Despite this, the pace of new finds has meant that it has an important collection.
Notes
References
*"100 objects"''A History of Ireland in 100 Objects''
''
An Post
(; literally 'The Post') is the state-owned provider of postal services in Ireland. An Post provides a "universal postal service" to all parts of the country as a member of the Universal Postal Union. Services provided include letter post, p ...
, The Irish Times
''The Irish Times'' is an Irish daily broadsheet newspaper and online digital publication. It launched on 29 March 1859. The editor is Ruadhán Mac Cormaic. It is published every day except Sundays. ''The Irish Times'' is considered a newspaper ...
'', National Museum of Ireland
The National Museum of Ireland ( ga, Ard-Mhúsaem na hÉireann) is Ireland's leading museum institution, with a strong emphasis on national and some international archaeology, Irish history, Irish art, culture, and natural history. It has thre ...
and the Royal Irish Academy
The Royal Irish Academy (RIA; ga, Acadamh Ríoga na hÉireann), based in Dublin, is an academic body that promotes study in the sciences, humanities and social sciences. It is Ireland's premier List of Irish learned societies, learned socie ...
, 2017
* Thomas Charles-Edwards, ''Early Christian Ireland'', Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
, 2000
Driscoll, K. The Early Prehistory in the West of Ireland: Investigations into the Social Archaeology of the Mesolithic, West of the Shannon, Ireland (2006)
* Herity, M. and G. Eogan. Ireland in Prehistory. (1996) Routledge. * Ó Cróinín, Dáibhí, ed. (2008). ''A New History of Ireland: Prehistoric and early Ireland'', (Volume 1 series), Oxford University Press, . * Wallace, Patrick F., O'Floinn, Raghnall eds. ''Treasures of the National Museum of Ireland: Irish Antiquities'', 2002, Gill & Macmillan, Dublin, The book is chapters of text, followed by commentary on the illustrations and then a section with the illustrations, cross-referred by chapter and picture numbers, e.g. "3:13"
Further reading
* * Barry, T. (ed.) A History of Settlement in Ireland. (2000) Routledge. . * Bradley, R. The Prehistory of Britain and Ireland. (2007) Cambridge University Press. . * Coffey, G. Bronze Age in Ireland (1913)Driscoll, K. The Early Prehistory in the West of Ireland: Investigations into the Social Archaeology of the Mesolithic, West of the Shannon, Ireland (2006).
* Flanagan L. Ancient Ireland. Life before the Celts. (1998). * Thompson, T. ''Ireland’s Pre-Celtic Archaeological and Anthropological Heritage.'' (2006) Edwin Mellen Press. . * Waddell, J., ''The Celticization of the West: an Irish Perspective'', in C. Chevillot and A. Coffyn (eds), L' Age du Bronze Atlantique. Actes du 1er Colloque de Beynac, Beynac (1991), 349–366. * Waddell, J.,''The Question of the Celticization of Ireland'', Emania No. 9 (1991), 5–16. * Waddell, J., 'Celts, Celticisation and the Irish Bronze Age', in J. Waddell and E. Shee Twohig (eds.), ''Ireland in the Bronze Age''. Proceedings of the Dublin Conference, April 1995, 158–169.
Irish Dark Age
*"A note on climatic deterioration in the first millennium BC in Britain", Stuart Piggot, ''Scottish Archaeological Forum'', iv, 1972, pp. 109–113 * "The Greek geographic tradition and Ptolemy's evidence for Irish geography", J.J. Tierney in ''Proceedings of theRoyal Irish Academy
The Royal Irish Academy (RIA; ga, Acadamh Ríoga na hÉireann), based in Dublin, is an academic body that promotes study in the sciences, humanities and social sciences. It is Ireland's premier List of Irish learned societies, learned socie ...
'', lxxvii, 1976, pp. 257–65
* "Dark Ages and the Pollen Record", D.A. Weir, ''Emania'' 11, 1993, pp. 21–30
* "Dark Ages and Dendrochronology", Mike Baillie, ''Emania'' 11, 1993, pp. 5–12
* "Cows, Ringforts and the Origins of Early Christian Ireland", F. McCormick, ''Emania'' 13, 1995, pp. 33–37
* "Iron-age Ireland", Barry Raftery in ''A New History of Ireland'' volume one, 2008, pp. 134–181
Archaeology
* Arias, J. World Prehistory 13 (1999):403–464.''The Origins of the Neolithic Along the Atlantic Coast of Continental Europe: A Survey. '' * Bamforth and Woodman, Oxford J. Arch. 23 (2004): 21–44. ''Tool hoards and Neolithic use of the landscape in north-eastern Ireland.'' * Clark (1970) ''Beaker Pottery of Great Britain and Ireland'' of the ''Gulbenkain Archaeological Series'', Cambridge University Press. *Genetics
* * *External links
Ask about Ireland, Flora and fauna
Postcards of the Prehistoric Monuments of Ireland
Treasures of early Irish art, 1500 B.C. to 1500 A.D.
an exhibition catalogue from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF)
Prehistoric Waterford
{{Europe topic , Prehistory of
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
History of Ireland by period
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
*